Purpose of Test
This test method assesses the ability of a textile to prevent growth of microorganisms. This evaluation estimates the antibacterial efficacy against various concentrations of microorganisms.
The parallel streak method is performed to qualitatively evaluate the bacteriostatic activity of diffusible antibacterial agents on treated textiles.
Through the years, this test has been used in providing evidence for antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Terminology Defined
Antibacterial Activity – Evaluates the protection a textile provides against microorganisms, biological fluids, and aerosols.
Bacteriostatic Activity – The capacity of the textile to resist bacteria growth.
Gram-positive Bacteria – Microorganisms with highly variable growth and resistance properties.
Gram-negative Bacteria – Infectious microorganisms that are highly resistant to most antibiotics.
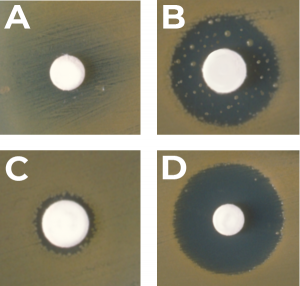
Zone of Inhibition – A circular area where the antibiotic agent was placed in which bacteria doesn’t grow.
Growth Agar – A culture medium used for growing microorganisms.
Test Method
Materials used for test
- Test specimen (treated and untreated)
- Antibacterial agent
- Petri dishes
- Sterile inoculating loop
Testing Procedure
The microorganisms are inoculated with distilled water and used to apply 5 parallel steaks to a solidified growth area. The fabrics are placed onto the streaks and gentle pressure is applied to ensure contact. The samples undergo an incubation period under a particular temperature to test the bacteriostatic activity.
Test Procedure (Summary)
Part 1: Preparation of the microorganism: The test microorganism is prepared in a liquid culture form. There are two microorganisms to be used:
- S. aureus
- K. penumoniae
Part 2: Solidification of sterilized molten growth agar. The sterilized molten growth agar is transferred into a sterile petri dish to solidify before inoculation.
Part 3: Test standardization. The test microorganisms are diluted with sterile distilled water.
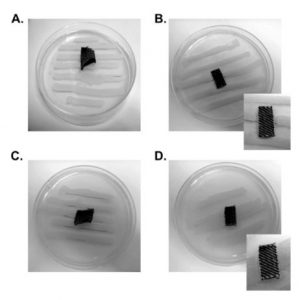
Part 4: Streak application: A sterile inoculating loop is used to apply five consecutive streaks onto the solidified growth agar. The space must be spaced evenly and the application should not need any refilling. Five parallel streaks must appear with different concentrations.
Part 5: Streak test: The treated test specimen cut in rectangular form with measurements of 25x55mm is positioned across the 5 parallels streaks. An untreated specimen should be tested alongside the treated samples.
Part 6: Pressure application: A gentle pressure is applied onto the samples to inflict contact of the textiles and the inoculated agar.
Part 7: Incubation of test samples: Both the treated and untreated test samples are put into an incubation period at a particular temperature. This is done to ensure optimal growth.
Part 8: Post-incubation evaluation: After the incubation period, the test samples are removed from the plates. The samples are measured by evaluating the present bacterial growth. A specific method formula is used to compute the zone of inhibition.