Purpose of Test
This test evaluates the resistance of fabrics to electrical current. This resistivity is influenced by the accumulation of electrostatic charge in fabric.
Terminology Defined
Electrical Resistivity – The measurement of how the fabric resists the electric current.
Electrostatic Charge – The deficiency or excess of electrons on a textile surface.
Electrical resistance meter – An electrical tool that measures the electrical resistance of surfaces. This can be an ohmmeter or megohmmeter.
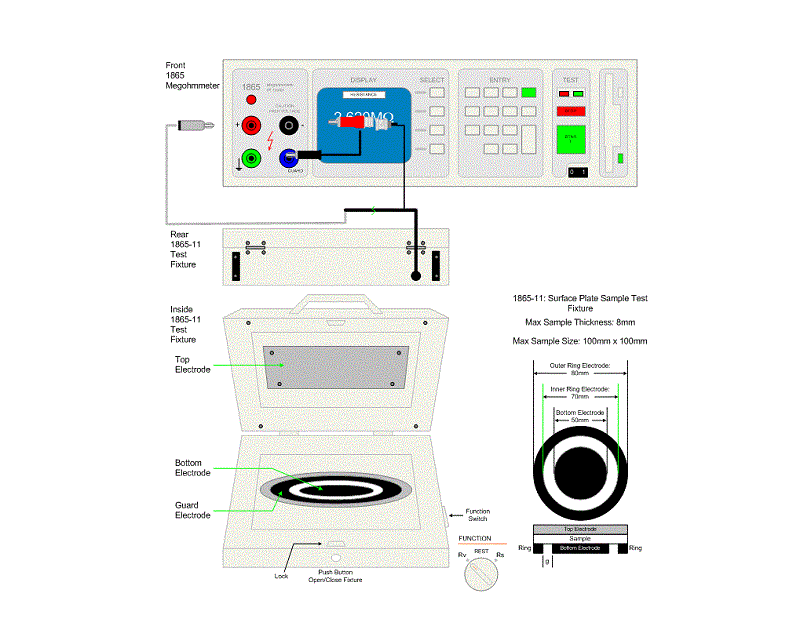
Standard Resistor – These are high-precision resistors used as a reference to calibrate and verify the accuracy of other resistors.
Test Method
Materials Used for Test
- Test specimen
- Ohmmeter
- Conditioning and Test Chamber
- Standard Resistors
- Radioactive Bar
- Rectangular Flat Metal Pieces
Testing Procedure
The electrical resistance of the fabric is measured with an electrical resistance meter given the test specimens are at equilibrium with certain atmospheric conditions of humidity and temperature.
Test Procedure (Summary)
Part 1: Preparation of the test specimen and electrical resistance meter: The test specimen is conditioned at pre-determined temperature and humidity. The electrical resistance meter is calibrated according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Part 2: Removal of static charges: The static charges on the fabric surface are removed by passing a radioactive bar over the textiles.
Part 3: Measurement of electrical resistance: The test specimen is put in contact with the electrode. The electrical resistance of the fabric is measured in length and width directions.