Purpose of Test
The AATCC 30 test method evaluates and compares the antifungal activity of textile materials like gauze, cloth, and similar objects.
This test method has two purposes:
- Determine textile’s susceptibility to mildew and rot.
- Measure the effectiveness of fungicides on textile materials.
Terminology Defined
Antifungal Activity – Evaluates the textile property to protect against fungi growth, like mildew and rot.
Growth Agar – A culture medium used for growing microorganisms.
Spore Suspension – Calibrated suspension of bacterial spores used for inoculation of products or preparation of sterilization process.
Zone of Inhibition – A circular area where the antibiotic agent was placed in which bacteria doesn’t grow.
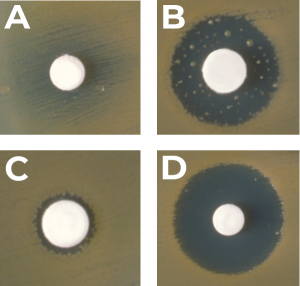
Test Method
Materials Used for Test
- Test specimens
- Petri dishes
- Sealed Jars
- Fungi
- Carbon source
Testing Procedure
The AATCC 30 test method has two different test types available:
- Test III – Agar Plate: This similarly works like the Antibacterial test where fungus growth is tested by inoculation and zone of inhibition.
- Test IV – Humidity Jar, Mixed Spore Suspension: This test type specializes in hydrophobic textiles.
Test Procedure (Summary)
AATCC 30 Test III – Agar Plate
Part 1: Preparation of fungus: The fungus, Aspergillus niger, is cultured in a medium and left to grow spore suspension at a given time.
Part 2: Preparation of agar medium: Depending on the test level, the agar medium is prepared in a petri dish with or without an additional carbon source.
Part 3: Inoculation of solid agar medium: The solid agar medium is inoculated with the spore suspension.
Part 4: Placement and incubation of test specimen: The test specimen is placed on top of the inoculated agar medium. Then, it will be placed in the inoculated spore suspension. The petri dishes are sealed and incubated for 7 or 14 days.
Part 5: Evaluation of antifungal activity: After the incubation period, the test samples are rated if they have:
- Macroscopic growth (visible to the eye)
- Microscopic growth (not visible to the eye)
- No growth
AATCC 30 IV – Humidity Jar, Mixed Spore Suspension
Part 1: Preparation of fungus: The type of fungi to be used is cultivated. The fungi that can be used include:
- Aspergillus niger
- Penicillium varians
- Trichoderma viride
Part 2: Preparation of spore suspension: The spore suspension is prepared by washing it according to a specified method.
Part 3: Saturation and inoculation of the test specimen: The test specimen and control fabrics are saturated in the fungi growth media. Each side of the saturated test and control fabrics are inoculated with the spore suspension.
Part 4: Incubation: The saturated fabrics are sealed in their individual jars for 14 or 28 days.
Part 5: Evaluation of antifungal activity: After the incubation period, the test samples are rated if they have:
- Macroscopic growth (visible to the eye)
- Microscopic growth (not visible to the eye)
- No growth